Position:Home >
Psoriasis - Vaginal Epithelial Mitotic Model
Psoriasis - Vaginal Epithelial Mitotic Model
Background
Psoriasis is a clinically common chronic, recurrent inflammatory skin disease characterized by skin lesions exhibiting abnormalities such as epidermal hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and thinning or disappearance of the granular layer. These abnormalities—particularly alterations in the stratum corneum—inevitably lead to impaired epidermal barrier function in psoriasis patients. However, skin infections are uncommon in psoriasis patients, a phenomenon that has attracted widespread attention.
Materials and methods
KM mice, 8 females, approximately 6 weeks old, self-bred
Model creation method: The model group received oral administration of estradiol benzoate at 9:00 AM daily for three consecutive days. Two hours after the final dose, mice received an intraperitoneal injection of colchicine. Five hours later, mice were euthanized, and vaginal tissue samples were collected.
Evaluation Criteria: Vaginal epithelial HE staining; Vaginal epithelial PCNA immunohistochemical staining.
Model creation method: The model group received oral administration of estradiol benzoate at 9:00 AM daily for three consecutive days. Two hours after the final dose, mice received an intraperitoneal injection of colchicine. Five hours later, mice were euthanized, and vaginal tissue samples were collected.
Evaluation Criteria: Vaginal epithelial HE staining; Vaginal epithelial PCNA immunohistochemical staining.
Test and verify
阴道上皮HE检测
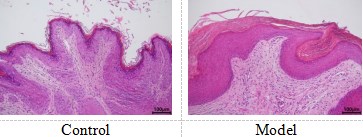
正常组上皮组织结构正常,除部分样本有少量炎性细胞浸润外,无明显病理变化;模型组上皮组织均可见基底层增厚,2号样本和8号样本有少量毛细血管增生,有模型趋势。
PCNA的免疫组化检测
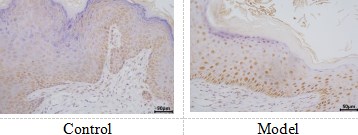
模型组基底层均可见有明显的PCNA阳性表达,模型有效。